Large Intestine Cancer
Info | Symptoms | Diagnosis | Treatment Options
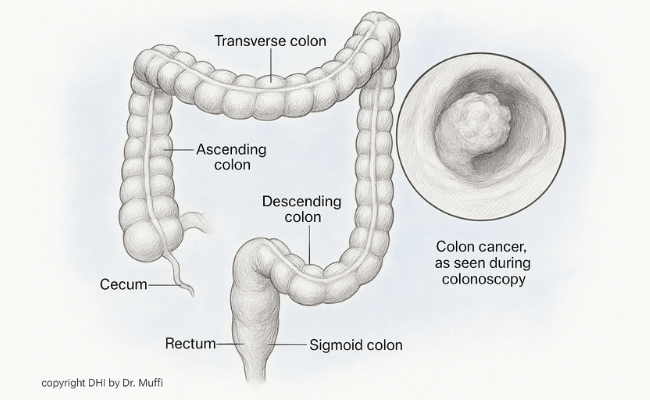
What You Need to Know
Large intestine cancer (commonly referred to as colorectal cancer) occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the colon or rectum. Early diagnosis and timely treatment are key to improving outcomes and quality of life.
Common Symptoms of Large Intestine Cancer
If you experience any of the following, consult your doctor:
- Changes in bowel habits (diarrhea, constipation, or narrowing of stool lasting more than a few days)
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal pain, cramping, or bloating
- Feeling of incomplete bowel emptying
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue or weakness
- Loss of appetite
Diagnosis & Evaluation
- Colonoscopy (with biopsy)
- Imaging scans (CT, MRI, PET)
- Blood tests (including CEA tumor marker)
- Stool tests (for occult blood or DNA changes)
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the location, stage, and spread of the cancer. A personalized plan may include:
Surgery (Primary Treatment for Most Patients)
- Colectomy (Colon Resection)
Partial Colectomy: Removal of the cancerous section of the colon along with nearby lymph nodes.
Total Colectomy: Removal of the entire colon in more extensive cases. - Proctectomy
Removal of part or all of the rectum (for rectal cancer). - Proctocolectomy with Ileostomy
Removal of both the colon and rectum, often followed by the creation of a stoma (ileostomy). - Colostomy or Ileostomy Creation
A stoma may be created temporarily or permanently, depending on the location and extent of surgery. - Transanal Minimally Invasive Surgery (TAMIS)
A less invasive approach for early-stage rectal cancers, performed through the anus without external incisions. - Pelvic Exenteration
A complex surgery for advanced rectal cancers that have spread to nearby organs, involving removal of the rectum and surrounding structures.
Other Treatments
- Chemotherapy: Before or after surgery to shrink tumors or kill remaining cancer cells.
- Radiation Therapy: Especially for rectal cancers, often combined with chemotherapy.
- Targeted Therapy & Immunotherapy: For advanced or metastatic cases, depending on tumor biology.




